Propel Water is marketed as a healthy flavored water containing electrolytes, vitamins, and minerals. In this article, we will examine the contents of Propel Water, assess its overall health benefits, and consider whether it is suitable for consumption on the carnivore diet.
What Is in Propel Water?
Propel Water is a brand of flavored water that is very low in calories while containing essential electrolytes, vitamins, and minerals. It caters to fitness and health-conscious consumers.
The main ingredient in Propel Water drinks is water but there are added vitamins (vitamin C, vitamin E, and B vitamins) and minerals (sodium, potassium and zinc). In addition, due to the absence of added sugar, Propel Water contains artificial sweeteners and flavors as well as preservatives to protect freshness. [1]
There are two types of Propel Water: Electrolyte Hydration and Immune Support. The main difference between these two types are their vitamin and mineral contents. Immune Support drinks have a slightly higher vitamin and mineral content than Electrolyte Hydration.
Below are examples of nutritional contents and ingredient lists for Electrolyte Hydration (berry flavor) and Immune Support (orange raspberry flavor) drinks.
Propel Water – Electrolyte Hydration
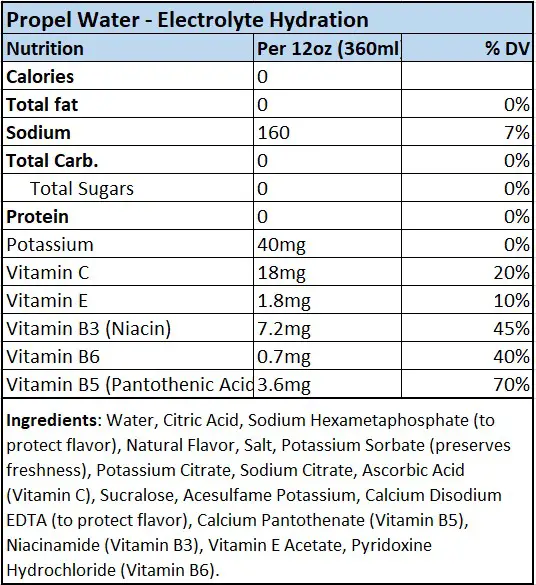
As can be seen in the above table, Electrolyte Hydration drinks contain water, electrolytes (sodium and potassium) and a few vitamins (vitamin C, vitamin E, vitamin B3, vitamin B5 and vitamin B6). In addition, artificial sweeteners, flavors and preservatives are also added.
Propel Water – Immune Support
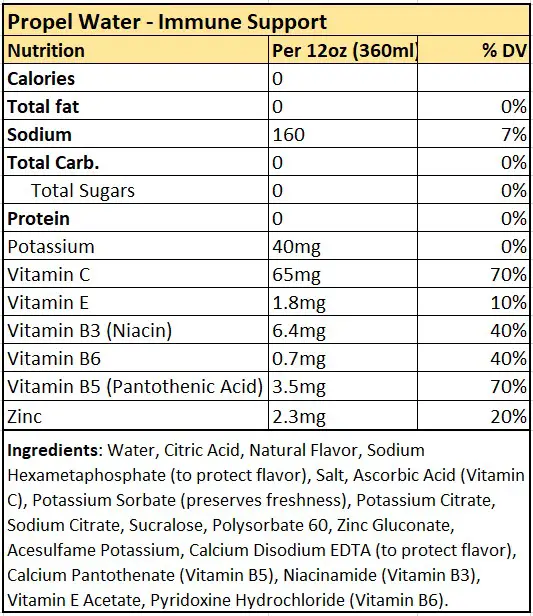
The nutritional content of Immune Support drinks is very similar to Electrolyte Hydration in that they both contain water, electrolytes and vitamins. However, Immune Support drinks have a slightly higher amount of vitamin C and zinc, which are both essential nutrients critical for immune function.
Is Propel Water Healthy?
In our opinion, Propel Water is not a healthy drink. Although it has no added sugar, it contains harmful ingredients such as artificial sweeteners, artificial flavors, and preservatives. Furthermore, currently, there is also no evidence suggesting that taking vitamin and mineral supplements offer health benefits. Some studies even show increased health risks from taking such supplements.
Artificial Sweeteners
In an effort to make hydration and sports drinks appeal to health-conscious consumers, manufacturers replace processed sugar with artificial sweeteners to keep these drinks low or zero in calories. However, emerging evidence suggest that artificial sweeteners such as sucralose and acesulfame potassium used in Propel Water may have serious health implications.
Sucralose
Sucralose (600 times sweeter than sugar) has been found to impair insulin sensitivity in healthy humans when consumed with carbohydrates, suggesting a potential dysregulation of gut-brain control of glucose metabolism. [2, 3]
Sucralose is also associated with an elevated risk of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular mortality, particularly in individuals who are overweight or obese. [4, 5]
In addition, sucralose contains a substance called sucralose-6-acetate, which has been shown to cause damage to DNA and is considered genotoxic. The amount of sucralose-6-acetate in a single daily drink sweetened with sucralose already surpass the threshold for concerns related to genotoxicity. [6]
Moreover, sucralose-6-acetate has been found to increase the expression of genes linked to inflammation, oxidative stress, and cancer and both sucralose-6-acetate and sucralose negatively impact the integrity of the intestinal barrier. [7]
In studies involving rats, sucralose led to alterations in gut microbiome composition, with a decrease in beneficial bacteria. Elevated concentrations of sucralose were found to be mutagenic, and high-temperature cooking with sucralose was reported to generate chloropropanols, a potentially toxic class of compounds. [8]
Acesulfame Potassium
Similar to sucralose, the consumption of acesulfame potassium (200 times sweeter than sugar) has been found to cause various health issues including changes in gut microbiota, metabolic disturbances, weight gain, increased cardiovascular risks, and increased cancer risk.
In animal studies, acesulfame potassium can disrupt gut microbiome, cause weight gain, negatively affect blood lipid profiles, and result in the hardening of the arteries. [9, 10]
In epidemiological studies, acesulfame potassium, along with other artificial sweeteners, has been associated with an elevated risk of cardiovascular disease, increased cancer risk, disruptions to gut microbiome, and intestinal injury. [11, 12, 13]
While the acesulfame potassium content in beverages such as Propel Water may be relatively low, it’s important to remember that artificial sweeteners are used extensively in thousands of food and beverage products. Cumulatively, the intake of these sweeteners can potentially reach an unsafe threshold, especially for those who consume a significant amount of processed foods and drinks on a regular basis.
In summary, there’s nothing sweet about artificial sweeteners. Although they may offer a slight reduction in calorie intake, the trade-off involves the potential ingestion of other chemicals that could be detrimental to your health. Moreover, existing evidence suggests that artificial sweeteners do not help with weight management. The World Health Organization advises against the use of artificial sweeteners for controlling body weight or mitigating the risk of noncommunicable diseases. [14, 15]
Preservatives
Propel Water contain preservatives like sodium hexametaphosphate, potassium sorbate, and calcium disodium EDTA to protect freshness and flavor of the drinks. Similar to artificial sweeteners, preservatives have been found to have adverse health impacts.
For example, high intake of potassium sorbate, known for its potent antimicrobial properties, can result in nutritional deficiency and cause genotoxic effects including DNA damages and lead to many chronic diseases, especially diabetes mellitus and cancers. [16, 17]
EDTA, another common preservative, is also of concern because it has the ability to bind to minerals (e.g. copper, iron, lead, zinc, calcium, manganese, and magnesium). Therefore, when consumed in larger quantities, EDTA may lead to the removal of essential minerals from the body. This could potentially result in mineral deficiencies, particularly in calcium, magnesium, iron, and zinc. Hence, prolonged and excessive use of EDTA-containing products could cause health concerns. [18, 19]
Citric Acid
Citric acid is a weak organic acid found naturally in citrus fruits, particularly in high concentrations in lemons and limes, but it’s also present in smaller amounts in oranges and other citrus fruits. Chemically, it is a tricarboxylic acid and is widely used in the food and beverage industry as a preservative and acidulant.
Citric acid’s sour taste makes it a common additive to various foods and drinks, providing a tart flavor. In addition to its culinary applications, citric acid has uses in various industries, including as a cleaning agent, a water softener, and in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries.
While citric acid is generally considered safe for human consumption, there are also several health concerns, including dental erosion, allergic reaction, and gastrointestinal irritation.
Citric acid, when consumed in high concentrations or frequency, may contribute to dental erosion. This is because citric acid is acidic and can soften tooth enamel over time. This effect is more relevant in products with high acidity, such as citrus fruits and some acidic beverages such as soft drinks and sport drinks. [20, 21]
Some individuals may be sensitive to high amounts of manufactured citric acid, leading to respiratory symptoms, joint pain, irritable bowel symptoms, muscular pain, and enervation. [22]
Added vitamins and minerals
As shown above, Propel Water contains added vitamins and minerals (such as vitamin E, B vitamins, zinc, and potassium) to enhance its nutritional profile and make it appear more healthy.
However, currently, there is insufficient evidence supporting the health benefits of vitamin and mineral supplementation. In fact, some studies indicate that consuming these supplements in the absence of nutritional deficiencies might even pose certain health risks. [23, 24, 25]
Can You Drink Propel Water on the Carnivore Diet?
The carnivore diet is a restrictive diet that includes only animal-based foods like beef, lamb, poultry, seafood, eggs, and fish, while omitting plant-based foods. Propel Water, being a flavored water product, typically contains additives like artificial sweeteners (such as sucralose and acesulfame potassium), citric acid, and natural flavors. Therefore, Propel Water should not be a part of a strict carnivore diet which aligns with the principles of consuming only foods our ancestors ate and drinking only water.
Moreover, as previously discussed, Propel Water, despite its low calorie and sugar content with added vitamins and minerals, is not considered a healthy option due to the presence of various potentially harmful chemicals, including artificial sweeteners and preservatives.
Although marketed toward health and fitness-conscious consumers as a means to replenish electrolytes lost during intense workouts, there are alternative and healthier ways to achieve this goal without regular exposure to harmful chemicals.
For instance, making your own electrolyte drinks using natural ingredients like water, lemon juice, salt, honey, and coconut water, can be a healthier alternative. Additionally, you can opt create electrolyte drinks using water, sea salt, and electrolyte powders (e.g. potassium citrate powder and magnesium malate). Homemade electrolyte solutions offer a much healthier choice compared to commercially available options.
Other posts you might be interested in:
Is Diet Coke Okay on the Carnivore Diet?
Do You Need Electrolyte Supplement on a Carnivore Diet?
Is Carnivore Diet + Fruit & Honey a Good Idea?
Why Animal-Based Protein Is Superior to Plant-Based Protein
10 Tips to Sneak More Organ Meat into Your Children’s Diet
Tips On Raising Children On a Carnivore or Animal-Based Diet
Carnivore vs Low-Carbs vs Moderate-Carbs vs High-Carbs
What Do Hardcore Carnivores Eat in a Day?
Disclaimer: The information in this post is for reference purposes only and is not intended to constitute or replace professional medical advice. Please consult a qualified medical professional before making any changes to your diet or lifestyle. Please check out our disclaimer for more detail.





