Being the most nutrient-dense food, organ meat is truly the superhero of the carnivore diet. But it is not for everyone, some people just can’t fathom the thought of eating the liver, kidneys, heart, tongue, or testicle of an animal.
So, do you have to eat organ meat on the carnivore diet to avoid suffering from some serious health consequences due to nutrient deficiencies?
The answer is it really depends.
If you are generally healthy, young and don’t have any chronic health conditions, and don’t like organ meat, you don’t have to eat it. Animal-based food sans organ meat still has everything that your body needs, from good quality protein and good fats to all essential vitamins and minerals.
However, if you have some chronic health problems that you’re seeking to resolve with the carnivore diet, you would definitely benefit from eating the most nutrient-dense food on the planet by incorporating organ meat into your diet.
Let’s look in more detail below at who may be fine without eating organ meat, who definitely should eat it, and what the alternatives to eating organ meat are for those who just can’t.
Who may be fine without eating organ meat?
If you are generally healthy and don’t suffer from any chronic health conditions, it’s fine to just eat animal-based food without eating organ meat.
This is because even in the absence of organ meat, animal-based food still can provide every nutrient that your body needs.
The table below, which provides the nutritional contents of six different animal-based foods, shows that even in this small sample, you can find every essential nutrient that your body needs, from good quality proteins and fats to all vitamins and minerals.
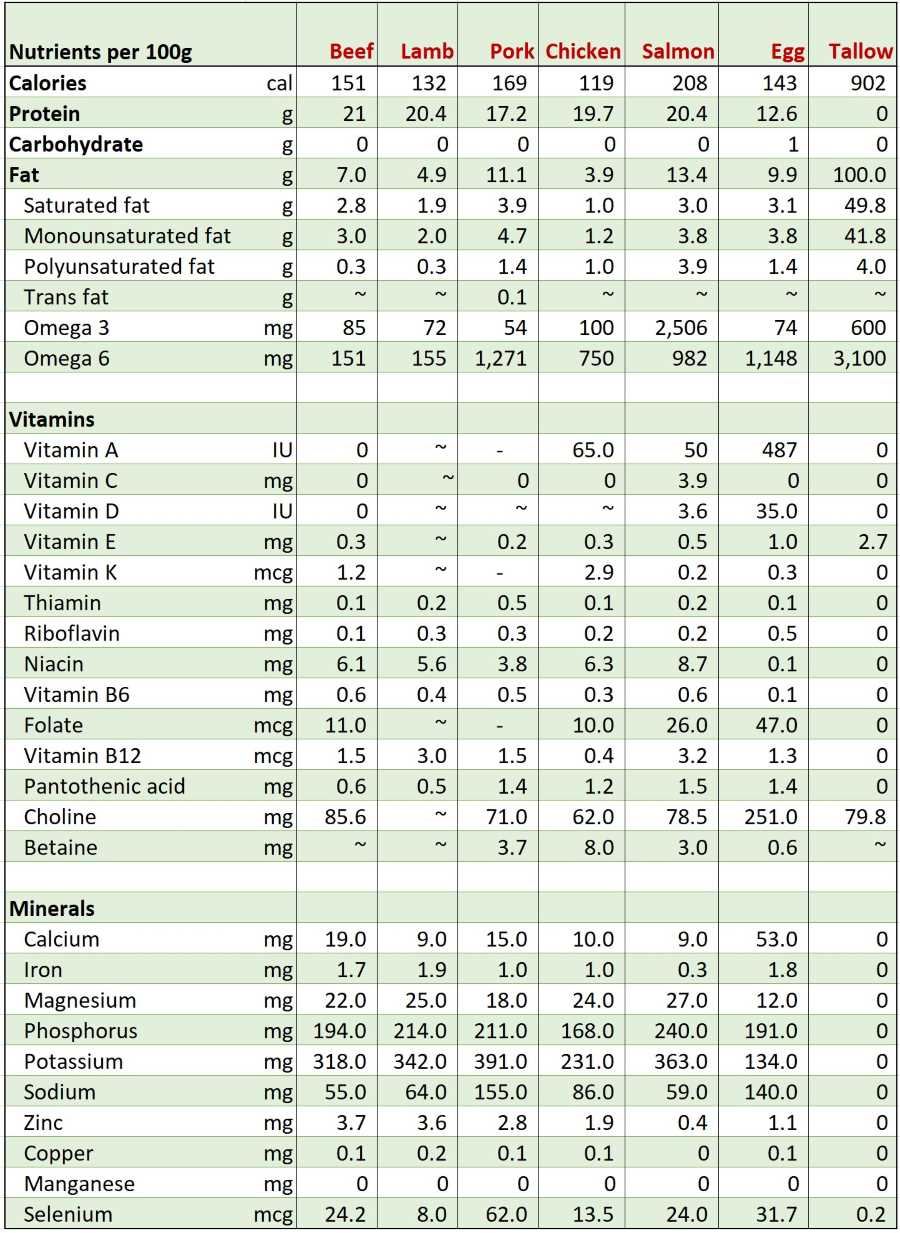
The table shows some nutrients have zero values but they either have only trace amounts or the USDA does not estimate them and assumes them to be zero.
For example, a study finds that 100 grams of grain-fed and grass-fed beef contain 1.6 grams and 2.5 grams of vitamin C respectively. The USDA, however, assumes a zero value for vitamin C in beef. [1, 2]
This small amount of vitamin C in muscle meat alone is enough to prevent you from developing scurvy on the carnivore diet.
Another study finds that there are 5.6 to 10.8 mcg of manganese per 100 grams for various beef cuts, whereas the USDA shows a rounded-up zero value. [3, 4]
Some of the nutrients in animal-based food do have low values and you may not meet the daily recommended intakes for these nutrients if you only eat meat.
However, it is important to note that these recommended daily values are aimed at the general population who are on a variety of diets that include a substantial percentage of plant food and processed food.
Although some nutrient values may be low in animal-based food, your body is able to absorb them much better compared to nutrients in plant-based food due to the absence of plant anti-nutrients.
Your body’s need for some nutrients on the carnivore diet may also be lower due to the low-PUFA and low-carb nature of this diet.
For example, glucose and vitamin C are known to compete for absorption. On the carnivore diet, there would be a negligible amount of carbohydrate and glucose intake to compete with vitamin C for absorption. Hence you don’t need a lot of vitamin C because whatever you consume would be utilized efficiently. [5, 6]
Similarly, when your diet is low in omega 6 (pro-inflammatory), you don’t need to consume as much omega 3 (anti-inflammatory).
Who should eat organ meat?
If your aim is to resolve some chronic health problems with the carnivore diet, you definitely should incorporate organ meat into your diet on a regular basis.
Your body is an incredible machine and, given the right conditions, it can do an amazing job of healing itself.
By eliminating plant toxins and feeding it with the most nutrient-dense food, you will be creating an optimal condition for your body to heal itself from health problems that even modern medicine has failed.
Although you may be able to heal yourself by just eating meat and drinking water, incorporating organ meat can help accelerate the process.
For people with urgent health problems to resolve like cancer or debilitating autoimmune conditions, they don’t have any time to lose so they need to give their bodies the best food possible and that means eating pasture-raised fatty meat and organ.
As can be seen in the table below, organ meat is the real superhero of the carnivore diet. They are much more nutrient-dense than muscle meat, especially the liver.
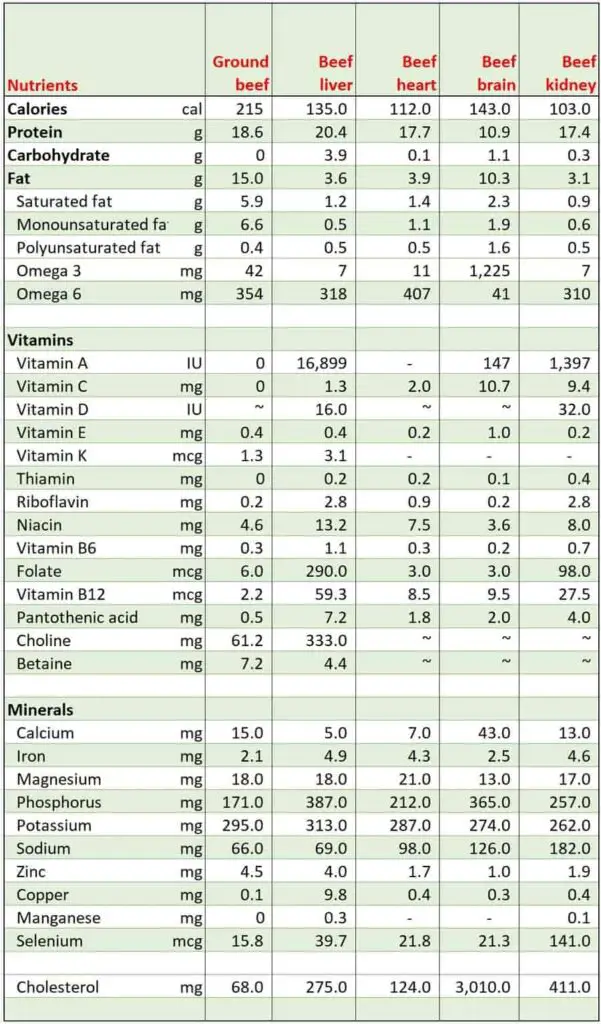
The International Center for Medical Nutritional Intervention (ICMNI) based in Hungary has used a high-fat animal-based diet, called the Paleolithic Ketogenic Diet, to successfully treat many chronic diseases including diabetes, autoimmune diseases, cancer, and intestinal permeability since 2012.
In their protocol, they recommend patients eat animal-based food including red and fatty meat, fat, and organ meat (e.g. brain, liver, kidney, and marrow) from four-legged animals.
The best food is red meat, animal fat, and organ meat from grazing animals, i.e. ruminants.
Organ meat intake is emphasized on this diet in order to maintain a healthy level of vitamins and minerals and you are encouraged to eat organ meat on a regular basis.
Alternatives to eating organ meat
Although many people know the value of organ meat, not everyone wants to or is able to eat organ meat.
If this is you, here are some ways to boost the nutritional content of your diet without actually eating organ meat.
- Eat eggs. The fact that eggs have everything needed to make a perfect little bird tells you how incredibly nutritious eggs are. If you have tested and found that you are okay with eggs, eat as many pasture-raised eggs as you want. But if you can only afford caged eggs, avoid them or eat them only occasionally
- Eat small fish. You’ll be eating the bones and the organs of the fish as well. Please get wild-caught fish if you can
- Eat other seafood like mussels, prawns, clams, and oysters, you are practically eating these animals “nose-to-tail” without knowing it
- Eat insects. If you can’t eat organ meat, you probably wouldn’t want to eat fried silk worms or crickets but you can buy them in powder form as well
- Eat a variety of animal-based food including ruminant, pork, chicken, and seafood but always look for pasture-raised and wild-caught sources if possible.
- Take desiccated organ supplements. Nothing beat fresh organ meat but if you can’t eat it, there are a lot of desiccated organ supplements available that you can buy.
Other posts you might be interested in
Do You Need Supplements on the Carnivore Diet?
The Paleolithic Ketogenic Diet and its Potential to Treat Chronic Diseases
Carnivore Diet vs Paleo Diet: Which One Is Better?
How Andrew Scarborough Put His Brain Cancer in Remission with an All-Meat Diet
How Pablo Kelly Beat Brain Cancer with a High-Fat Meat-Based Diet
Disclaimer: The information in this post is for reference purposes only and not intended to constitute or replace professional medical advice. Please consult a qualified medical professional before making any changes to your diet or lifestyle.





